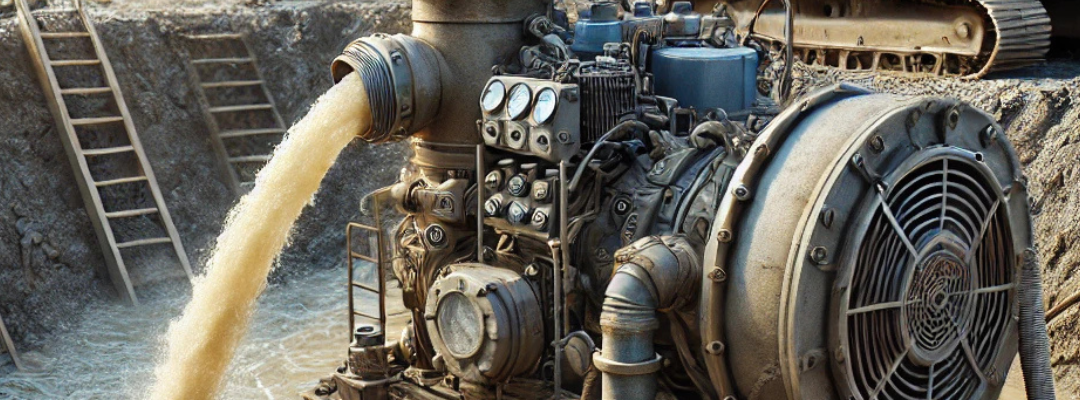
Properties and Importance of a Dewatering Pump
A dewatering pump is designed to remove water from construction sites, mines, underground tunnels, basements, or any area where excess water accumulation poses a problem. These pumps are essential for keeping work environments safe, dry, and operational, preventing flooding, and protecting infrastructure from water damage.
Key Properties of a Dewatering Pump:
- High Flow Rate (Capacity)
- Dewatering pumps are typically designed to handle large volumes of water quickly, often measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or cubic meters per hour (m³/h). The flow rate is a critical property since the pump needs to evacuate water as efficiently as possible to prevent water buildup.
- Flow rates for dewatering pumps can range from 100 to 5000 GPM (or 0.5 to 20 m³/h), depending on the size and application of the pump.
- Head (Lift Height or Total Dynamic Head – TDH)
- The head is the vertical distance the pump can lift water. Dewatering pumps need sufficient head to transport water from the sump or pit to the discharge point, which could be above ground or at a distant location.
- The Total Dynamic Head (TDH) includes the vertical lift plus any friction losses in the pipes, fittings, or hoses. Dewatering pumps generally have head ranges from 10 to 100 meters (33 to 330 feet).
- Portability and Mobility
- Dewatering pumps are often designed to be portable and easy to move to different locations. This is especially important in construction, mining, or emergency applications where rapid deployment is needed.
- Many dewatering pumps come with lightweight frames, handles, or are mounted on skids or trailers for easy transportation and setup.
- Pump Type There are different types of dewatering pumps, each suited to specific applications:
- Centrifugal Dewatering Pumps: The most common type, suitable for removing water with low to moderate solid content. They work well in construction sites, basements, and flooded areas.
- Submersible Pumps: Designed to operate fully submerged in water, ideal for pumping water from deep pits, wells, or sumps. Submersible dewatering pumps are commonly used in mining, construction, and municipal applications.
- Diaphragm Pumps: Used for heavy-duty applications and can handle more viscous fluids or fluids with higher solid content. These pumps are often air-operated and are suitable for muddy or debris-laden water.
- Trash Pumps: These are a subtype of centrifugal pumps that can handle water containing debris, such as leaves, twigs, or sand, making them useful in stormwater or construction dewatering tasks.
- Solids Handling Capacity
- Dewatering pumps often need to handle water containing silt, mud, sand, or other debris. Many dewatering pumps are designed with impellers and passages capable of passing solid particles without clogging.
- Trash pumps or diaphragm pumps are typically used in environments where water may contain large debris. They are designed to pump both water and solids without jamming.
- Durability and Corrosion Resistance
- Dewatering pumps are built from materials such as stainless steel, cast iron, or aluminum to ensure durability and resistance to corrosion in wet and potentially chemically aggressive environments.
- Rubber-lined pumps or abrasion-resistant materials are used in high-wear applications, such as handling slurry, sand, or abrasive particles.
- Self-Priming Capabilities
- Self-priming pumps are advantageous in dewatering applications, allowing the pump to automatically remove air from the suction line and start pumping water without manual intervention. This feature is useful in construction and emergency applications where speed and ease of use are critical.
- Energy Source
- Dewatering pumps can be powered by electric motors, diesel engines, or gasoline engines. The choice of energy source depends on the location and the availability of power:
- Electric Dewatering Pumps: These are commonly used in areas where electricity is readily available, such as urban construction sites, basements, or industrial facilities.
- Diesel or Gasoline-Powered Pumps: These are used in remote areas, large construction sites, or emergency situations where electricity is not available.
- Dewatering pumps can be powered by electric motors, diesel engines, or gasoline engines. The choice of energy source depends on the location and the availability of power:
- Sealing Mechanism
- Dewatering pumps need reliable sealing mechanisms to prevent water from entering sensitive components, such as the motor or engine. Mechanical seals, often made of carbon, ceramic, or silicon carbide, are commonly used to ensure long-lasting performance under wet conditions.
- Automatic Operation (Float Switch)
- Many dewatering pumps, especially submersible ones, are equipped with float switches that automatically start or stop the pump based on the water level. This prevents dry running and ensures the pump operates only when necessary, saving energy and reducing wear.
- Noise and Vibration Levels
- Some dewatering pumps, especially those used in urban or residential areas, are designed for low noise and minimal vibration. Electric submersible pumps tend to operate more quietly than engine-driven pumps, making them suitable for noise-sensitive environments.
Importance of a Dewatering Pump:
- Flood Prevention and Water Management
- Dewatering pumps play a critical role in flood prevention by quickly removing excess water from basements, construction sites, and flooded areas. This helps avoid property damage and ensures safe working conditions.
- In areas prone to flooding or heavy rainfall, dewatering pumps can be used to drain stormwater from public spaces, parking lots, or municipal areas, reducing the risk of flooding and maintaining infrastructure integrity.
- Construction Site Safety and Efficiency
- Construction sites often accumulate water due to rain, high groundwater levels, or nearby bodies of water. Dewatering pumps help remove this water, ensuring that foundations, trenches, and excavations remain dry and safe for workers.
- Dewatering pumps increase project efficiency by preventing delays caused by water buildup. Without proper dewatering, construction work could be slowed down or halted, leading to costly delays.
- Mining Operations
- In mining operations, dewatering pumps are used to remove water from mine shafts, tunnels, and pits, ensuring that the mining area remains dry and safe for workers and equipment.
- Underground mining operations often face the challenge of water inflow from underground sources, which could flood the mine if not controlled. Dewatering pumps ensure uninterrupted mining activities and protect expensive machinery from water damage.
- Maintaining Agricultural Land
- Dewatering pumps are also used in agriculture to manage waterlogged fields or drain excess water from irrigation systems, ponds, or canals. This is critical for maintaining crop health and preventing soil erosion or waterlogging.
- Proper dewatering helps improve the productivity of agricultural land, particularly after heavy rainfall or flooding, ensuring that crops receive optimal water levels.
- Disaster Response and Emergency Situations
- Dewatering pumps are essential tools in emergency response during flooding events, storms, or natural disasters. They are deployed to quickly remove water from residential areas, public infrastructure, and critical facilities like hospitals or schools.
- In disaster situations, portable and high-capacity dewatering pumps help mitigate the effects of flooding, reduce damage, and speed up recovery efforts.
- Preventing Structural Damage
- Accumulation of water can lead to structural damage, such as weakening of foundations, erosion of soil around buildings, or destabilization of retaining walls. Dewatering pumps prevent water-related structural failures by removing water before it causes serious damage.
- Dewatering is especially important in underground constructions such as basements, parking garages, or tunnels, where water intrusion can pose a significant risk to the structural integrity of the building.
- Environmental Protection
- Dewatering pumps are often used in environmental cleanup efforts, such as removing contaminated water from industrial spills or chemical accidents. They help contain hazardous materials and prevent further spread into surrounding soil or water bodies.
- In water treatment plants, dewatering pumps are used to remove water from sludge, facilitating the separation of solid waste from treated water.
- Maintaining Reservoir and Canal Levels
- In water management systems, dewatering pumps help maintain water levels in reservoirs, canals, or irrigation systems by removing excess water and redistributing it as needed. This ensures the efficient use of water resources in both urban and agricultural settings.
Conclusion:
Dewatering pumps are essential tools for managing water in various industrial, construction, mining, and emergency applications. Their ability to efficiently remove large volumes of water, handle solids, and operate under challenging conditions makes them indispensable for preventing flooding, ensuring safety, and maintaining operational efficiency. By selecting the right dewatering pump based on flow rate, head, and environmental conditions, operators can optimize water management and protect both infrastructure and workers from the hazards of water accumulation.