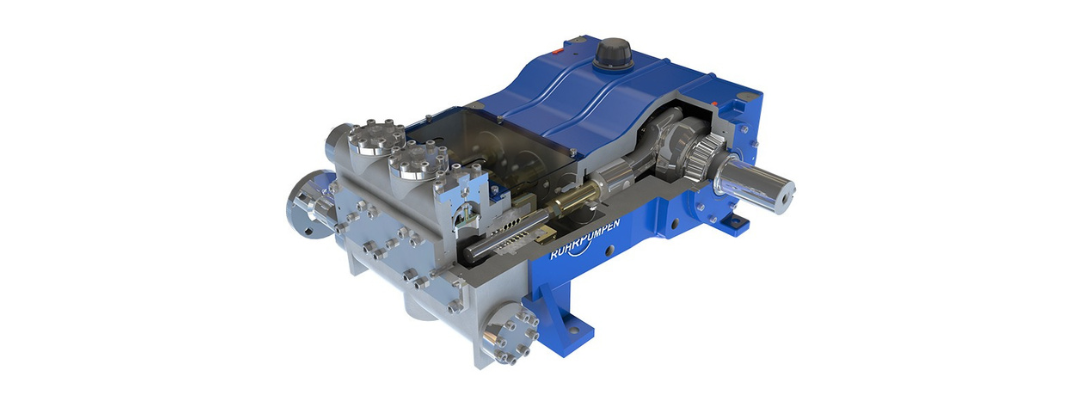
Reciprocating pumps are positive displacement pumps that use a piston or plunger to move fluids through a system by repeatedly creating suction and discharge strokes. These pumps are known for their ability to generate high pressure, handle viscous and abrasive fluids, and deliver precise flow rates, making them ideal for a wide range of industrial and commercial applications.
Key Applications of Reciprocating Pumps:
1. Oil and Gas Industry
- Application: Reciprocating plunger pumps are widely used in oil and gas extraction, refining, and transportation. They are particularly useful for injecting chemicals, pumping oil, and handling high-pressure applications.
- Uses:
- Chemical Injection: Reciprocating pumps are used to inject chemicals like corrosion inhibitors, biocides, or hydrate inhibitors into oil and gas pipelines to protect the system from corrosion, freezing, and blockages.
- Well Drilling and Fracturing: Reciprocating pumps are used in high-pressure applications such as hydraulic fracturing (fracking) and well drilling.
- Crude Oil Transfer: These pumps handle the transfer of crude oil and other fluids through pipelines at high pressures.
- Benefits:
- Can handle high pressures and viscous fluids.
- Provides precise and controlled flow rates, essential for chemical dosing.
2. Water Supply and Distribution
- Application: Reciprocating pumps are used in municipal water supply systems and rural water distribution networks to deliver water to elevated locations or over long distances.
- Uses:
- High-Pressure Water Supply: They are ideal for applications requiring high-pressure water delivery, such as in water treatment plants, distribution systems, and high-rise buildings.
- Pumping Water from Wells: Reciprocating pumps are used to lift water from deep wells in areas where submersible pumps are not suitable.
- Benefits:
- Efficient at delivering water over long distances or to high elevations.
- Reliable for providing steady, controlled water flow in remote areas.
3. Power Generation Plants
- Application: Reciprocating pumps are used in thermal, nuclear, and hydroelectric power plants for high-pressure applications, such as boiler feed, cooling water, and condensate extraction.
- Uses:
- Boiler Feed Pumps: In power plants, reciprocating pumps provide high-pressure water to boilers, ensuring efficient steam generation.
- High-Pressure Cleaning: Reciprocating pumps are used to clean various components in power plants, including heat exchangers and boilers.
- Benefits:
- Capable of generating very high pressures.
- Provides reliable performance in critical applications such as boiler feed.
4. Hydraulic Power Systems
- Application: In hydraulic power systems, reciprocating pumps are used to supply pressurized hydraulic fluid to operate hydraulic motors, cylinders, and other machinery.
- Uses:
- Hydraulic Jacks and Lifts: Reciprocating pumps power hydraulic jacks, presses, and lifts used in construction, manufacturing, and automotive applications.
- Hydraulic Systems in Heavy Machinery: These pumps are integral to the operation of hydraulic systems in excavators, cranes, and other heavy equipment.
- Benefits:
- Provides high pressure and precise control, ideal for lifting heavy loads or operating hydraulic tools.
- Efficient in delivering the required force in hydraulic circuits.
5. Industrial Chemical Processing
- Application: Reciprocating pumps are essential in the chemical industry for transferring and metering chemicals. Their precise flow control and ability to handle corrosive and viscous fluids make them ideal for chemical dosing and injection processes.
- Uses:
- Metering and Dosing: Reciprocating pumps are used to meter and inject precise amounts of chemicals in various processes, such as in the production of fertilizers, pharmaceuticals, and petrochemicals.
- Corrosive Fluid Transfer: These pumps can handle aggressive or corrosive chemicals, making them suitable for transferring acids, solvents, and other industrial chemicals.
- Benefits:
- Accurate and controlled fluid flow, essential for maintaining process integrity.
- Can handle a wide range of fluid viscosities and corrosive properties.
6. Food and Beverage Industry
- Application: Reciprocating pumps are used in the food and beverage industry for transferring ingredients, dosing additives, and processing viscous materials like syrups, pastes, and purees.
- Uses:
- Ingredient Transfer: Reciprocating pumps transfer viscous ingredients, such as honey, molasses, or fruit purees, in food processing plants.
- Dosing Additives: They are also used to precisely dose flavors, colorants, or preservatives into food and beverage products during manufacturing.
- Benefits:
- Can handle thick, viscous fluids while maintaining consistent flow rates.
- Provides precise control for dosing small amounts of additives, ensuring product quality.
7. Pharmaceutical Industry
- Application: Reciprocating pumps are critical for pharmaceutical manufacturing, especially in processes requiring precise dosing, metering, and sterile fluid transfer.
- Uses:
- Dosing and Metering: These pumps are used to dose active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and other chemicals during the drug manufacturing process.
- Sterile Fluid Transfer: Reciprocating pumps are used in processes where sterile and contamination-free fluid handling is required, such as in the production of injectable drugs and vaccines.
- Benefits:
- Provides precise control over the flow of fluids, ensuring accuracy in pharmaceutical production.
- Suitable for handling high-purity or sterile fluids in cleanroom environments.
8. Sewage and Slurry Handling
- Application: Reciprocating pumps are used in wastewater treatment plants and other industrial settings to handle sewage, sludge, and slurry. Their ability to handle high-viscosity fluids and solids makes them suitable for these demanding applications.
- Uses:
- Sludge Transfer: Reciprocating pumps are used to transfer sludge and slurry in wastewater treatment processes, where high solids content can make pumping difficult for other types of pumps.
- Sewage Pumping: They are also used in sewage pumping stations, where they move wastewater and sewage to treatment plants.
- Benefits:
- Can handle abrasive, viscous, and solid-laden fluids.
- Provides reliable operation in challenging environments with heavy solids content.
9. High-Pressure Cleaning Systems
- Application: Reciprocating pumps are commonly used in high-pressure cleaning systems for industrial, commercial, and residential applications. These pumps generate the necessary pressure to power pressure washers and cleaning equipment.
- Uses:
- Pressure Washers: Reciprocating pumps are used in pressure washers to deliver water at high pressures, enabling efficient cleaning of surfaces like concrete, machinery, vehicles, and industrial equipment.
- Industrial Cleaning: These pumps are used for cleaning heat exchangers, tanks, pipes, and other industrial equipment that requires high-pressure water for cleaning.
- Benefits:
- Capable of delivering very high pressure for effective cleaning.
- Suitable for continuous operation in heavy-duty cleaning applications.
10. Marine Industry
- Application: In the marine industry, reciprocating pumps are used in a variety of shipboard systems, including ballast systems, bilge pumping, and engine cooling.
- Uses:
- Bilge Pumps: Reciprocating pumps are used to pump water from the bilge of a ship, ensuring that the vessel remains afloat by removing unwanted water.
- Ballast Pumps: They are also used to transfer ballast water in and out of the ballast tanks, helping to maintain the stability of the ship.
- Benefits:
- Reliable performance in marine environments with variable fluid conditions.
- Capable of handling seawater, oily bilge water, and other fluids.
11. Mining Industry
- Application: Reciprocating pumps are used in mining operations to pump slurries, transport water, and inject chemicals in processes such as ore extraction, beneficiation, and tailings management.
- Uses:
- Slurry Pumping: These pumps handle abrasive slurries containing ores, minerals, and sediments in mining operations.
- Dewatering: Reciprocating pumps are used for dewatering mines, removing water to ensure safe and efficient mining operations.
- Benefits:
- Durable and capable of handling highly abrasive and corrosive fluids.
- Provides the necessary pressure for long-distance fluid transfer.
Advantages of Reciprocating Pumps:
- High Pressure Handling: Reciprocating pumps can generate high pressures, making them ideal for applications where fluids need to be moved over long distances or against significant resistance.
- Precise Flow Control: These pumps provide accurate and controlled flow rates, making them suitable for metering and dosing applications where precision is critical.
- Handling of Viscous and Abrasive Fluids: Reciprocating pumps can handle a wide range of fluid viscosities, from thin liquids to thick slurries, as well as fluids containing solids and abrasives.
- Self-Priming: Many reciprocating pumps are self-priming, allowing them to start pumping without needing to be filled with fluid first.
- Flexibility in Application: Reciprocating pumps can be used in a variety of industries and applications, from chemical processing to wastewater treatment and industrial cleaning.